Catalog # |
Size |
Price |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 010-50 | 100 µg | $299 |
 )
)
|
Pro-His-Ala-Gln-Leu-Leu-Arg-Val-Gly-Cys-Val-Leu-Gly-Thr-Cys-Gln-Val-Gln-Asn-Leu-Ser-His-Arg-Leu-Trp-Gln-Leu-Val-Arg-Pro-Ala-Gly-Arg-Arg-Asp-Ser-Ala-Pro-Val-Asp-Pro-Ser-Ser-Pro-His-Ser-Tyr-NH2
|
|
Disulfide bridge(s): Cys10-Cys15
|
| 5200.96 | |
|
| ≥ 95% |
|
| Exhibits correct molecular weight |
|
| Insoluble in water. Dissolve in 30-40 µl of 50% acetonitrile in water. Then dilute with water or any desired buffer. |
|
|
Up to 6 months in lyophilized form at 0-5°C. For best results, rehydrate just before use. After rehydration, keep solution at +4°C for up to 5 days or freeze at -20°C for up to 3 months. Aliquot before freezing to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
|
| White powder |
|
| Each vial contains 100 µg of NET peptide. |
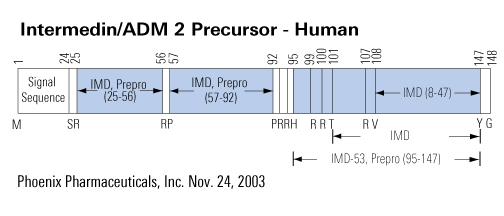
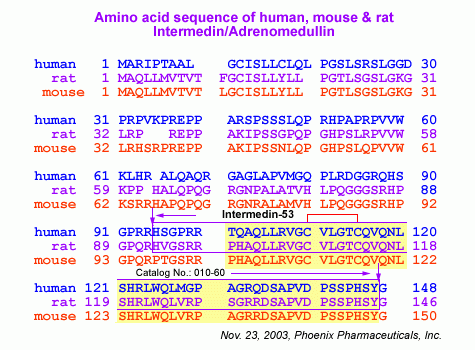

Intermedin (IMD) is a novel member of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide (CT/CGRP) family identified from human and other vertebrate tissues. Preprointermedin (preproIMD) can generate a 47 amino acid mature peptide (IMD(1-47)) and a shorter 40 amino acid one (IMD(8-47)) by proteolytic cleavage. Amino acid sequence analysis showed that cleavage sites are located between two basic amino acids at Arg93-Arg94, resulting in the production of preproIMD(95-147), namely IMD(1-53). The present study was designed to observe the effects of IMD(1-53) on cardiac function in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in isolated rat hearts. Perfusion with high-dose IMD(1-53) gave higher left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP) and maximal rate of increase and decrease of left ventricle pressure (+/-LVdP/dt(max)), and coronary perfusion flow (CPF) than those of controls. Cardiac I/R induced a marked inhibition of cardiac function and myocardial injury. Reperfusion with IMD(1-53) significantly ameliorated the inhibited cardiac function and bradycardia induced by I/R. Compared with the I/R-treatment alone, IMD(1-53) reperfusion augmented CPF, LVSP, and maximal rate of increase and decrease of left ventricle pressure (+/-LVdP/dt(max)) and decreased LVDP. In addition, reperfusion with IMD(1-53)markedly attenuated the leakage of lactate dehydrogenase and malondialdehyde content in myocardia compared with I/R alone. Reperfusion with IMD(1-53)increased the content of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in comparison with I/R alone. Interestingly, the above IMD(1-53) effects are similar to those of adrenomedullin. These results suggest that IMD(1-53), like adrenomedullin, has cardioprotective effects against myocardial I/R injury.
Yang JH, Jia YX, Pan CS, et al. Effects of intermedin(1-53) on cardiac function and ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;327(3):713-9.
Intermedin (IMD) is a novel member of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide (CT/CGRP) family identified from human and other vertebrate tissues. Preprointermedin can generate a 47-amino acid mature peptide (IMD(1-47)) and a shorter 40-amino acid one (IMD(8-47)) by proteolytic cleavage. The present study was designed to determine the protective effect of IMD on cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and its possible mechanism. Isolated rat hearts were perfused on a Langendorff apparatus and subjected to 45-min global ischemia and 30-min reperfusion. Cardiac function was measured. The release of myocardial protein and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA) were assayed. Myocardial cAMP content was determined by radioimmunoassay (RIA). Cardiac I/R induced a marked inhibition of cardiac function and myocardial injury. Reperfusion with IMD significantly attenuated the I/R injury. Compared with I/R alone, perfusion with 10(-8)mol/L IMD(1-47) and IMD(8-47) induced a 36% and 33% increase in Delta left ventricular pressure (DeltaLVP), 30% and 28% in maximal rate of increase of LV pressure (+LVdP/dt max), and 34% and 31% in maximal rate of decrease of LV pressure (-LVdP/dt max), respectively (all P<0.01) but an approximately 58% and 51% decrease in LV diastolic pressure, respectively (P<0.01). In addition, perfusion with IMD markedly attenuated the leakage of LDH, total protein and myoglobin from myocardia compared with I/R alone. The contents of ventricular myocardia cAMP after reperfusion with 10(-8)mol/L IMD(1-47) and IMD(8-47) were 130% and 91% higher, respectively, than that with I/R alone (all P<0.01). However, formations of myocardial MDA were 52% and 50% lower than that with I/R alone (all P<0.01), respectively. Interestingly, the above IMD effects were similar to those of adrenomedullin (10(-8)mol/L). These results suggest that IMD, like adrenomedullin, exerts cardio-protective effects against myocardial I/R injury.
Yang JH, Qi YF, Jia YX, et al. Protective effects of intermedin/adrenomedullin2 on ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Peptides. 2005;26(3):501-7.
Calcitonin, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), adrenomedullin (ADM), and amylin belong to a unique group of peptide hormones important for homeostasis in diverse tissues. Calcitonin is essential for calcium balance whereas CGRP and ADM are important for neurotransmission, and cardiovascular and respiratory regulation. Based on phylogenetic analysis, we identified intermedin as a novel member of the calcitonin/CGRP peptide family. Analysis of intermedin expression indicated that intermedin is expressed primarily in the pituitary and gastrointestinal tract. Intermedin increases cAMP production in SK-N-MC and L6 cells expressing endogenous CGRP receptors and competes with labeled CGRP for binding to its receptors in these cells. In addition, treatment of 293T cells expressing recombinant calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) and one of the three receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) showed that a CRLR/RAMP receptor complex is required for intermedin signaling. In contrast to CGRP and ADM, which exhibit a preferential stimulation of CRLR when coexpressed with RAMP1 and RAMP2 or RAMP3, respectively, intermedin represents a nonselective agonist for the RAMP co-receptors. In vivo studies demonstrated that intermedin treatment leads to blood pressure reduction in both normal and spontaneously hypertensive rats via interactions with the CRLR/RAMP receptors. Furthermore, in vivo treatment in mice with intermedin leads to a suppression of gastric emptying activity and food intake. Thus, identification of intermedin as a novel member of the calcitonin/CGRP peptide family capable of signaling through the CRLR/RAMP receptor complexes provides an additional player in the regulation of peripheral tissues by CRLR, and will allow development of new therapeutic agents for pathologies associated with diverse vascular and gastrointestinal disorders.
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C, Hsu SY. Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(8):7264-74.
| Catalog# | Product | Size | Price | Buy Now |
|---|
Social Network Confirmation