Catalog # |
Size |
Price |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 014-22 | 100 µg | $152 |
 )
)
|
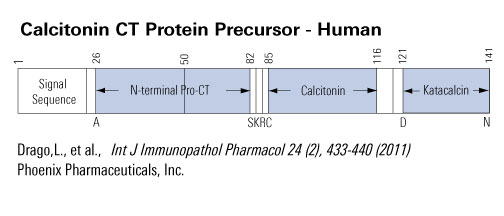
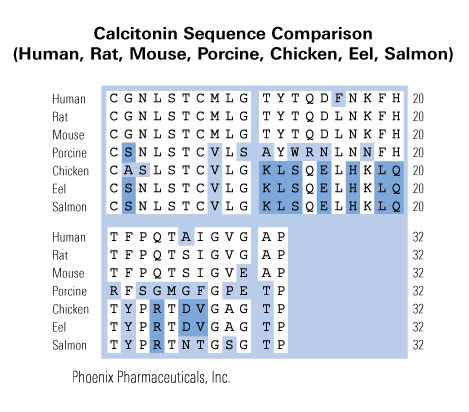
Cys-Gly-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys-Met-Leu-Gly-Thr-Tyr-Thr-Gln-Asp-Leu-Asn-Lys-Phe-His-Thr-Phe-Pro-Gln-Thr-Ser-Ile-Gly-Val-Glu-Ala-Pro-NH2
|
|
Disulfide bridge(s): Cys1-Cys6
|
| 3471.94 | |
|
| ≥ 95% |
|
| Exhibits correct molecular weight |
|
| Soluble in 20% acetonitrile in water. |
|
|
Up to 6 months in lyophilized form at 0-5°C. For best results, rehydrate just before use. After rehydration, keep solution at +4°C for up to 5 days or freeze at -20°C for up to 3 months. Aliquot before freezing to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
|
| White powder |
|
| Each vial contains 100 µg of NET peptide. |
  |
 |
In women, menopause refers to a series of physiological and mental symptoms of distress that result from a decrease in 17β-estradiol. In addition to the loss of fertility, the symptoms include facial flushing, depression, osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction, and genitourinary atrophy. Cirsium japonicum var. maackii is a perennial herbaceous species found in the mountains and fields of Korea, China, and Japan. The medicinal uses of C. japonicum include antioxidant, antidiabetic, antitumor, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory activities. We investigated the effect of C. japonicum extract in a rat model of menopause that exhibited rapid estrogen decline induced by ovariectomy (OVX rats). The rats were treated with C. japonicum extract for 10 weeks and the following parameters were measured: food intake, feed efficiency, body weight, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, liver weight, 17β-estradiol, uterus weight, AST, ALT, bone mineral density (BMD), bone alkaline phosphatase, calcitonin, and osteocalcin. In OVX rats, the administration of 50 and 100 mg kg-1C. japonicum extract significantly decreased body weight, total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol and significantly increased 17β-estradiol and BMD. During the light/dark box test, the C. japonicum treatment group (100 mg kg-1) spent more time in the light chamber than in the dark area, which was reflective of their diurnal nature. Using a molecular docking simulation, we predicted the plausible binding mode of the active compounds of C. japonicum with the ligand binding domain of estrogen receptor (ER)-α and ER-β. These results showed that C. japonicum extract can treat the symptoms before and after the menopause.
This Publication used the Rat Calcitonin EIA kit (RK-014-06) from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for measurement of calcitonin concentration.
Park JY, Yun H, Jo J, et al. Beneficial effects of Cirsium japonicum var. maackii on menopausal symptoms in ovariectomized rats. Food Funct. 2018;9(4):2480-2489.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) analogs have been associated with an increased incidence of thyroid C-cell hyperplasia and tumors in rodents. This effect may be due to a GLP1 receptor (GLP1R)-dependent mechanism. As the expression of GLP1R is much lower in primates than in rodents, the described C-cell proliferative lesions may not be relevant to man. Here, we aimed to establish primary thyroid cell cultures of rat and human to evaluate the expression and function of GLP1R in C-cells. In our experiments, GLP1R expression was observed in primary rat C-cells (in situ hybridization) but was not detected in primary human C-cells (mRNA and protein levels). The functional response of the cultures to the stimulation with GLP1R agonists is an indirect measure of the presence of functional receptor. Liraglutide and taspoglutide elicited a modest increase in calcitonin release and in calcitonin expression in rat primary thyroid cultures. Contrarily, no functional response to GLP1R agonists was observed in human thyroid cultures, despite the presence of few calcitonin-positive C-cells. Thus, the lack of functional response of the human cultures adds to the weight of evidence indicating that healthy human C-cells have very low levels or completely lack GLP1R. In summary, our results support the hypothesis that the GLP1R agonist-induced C-cell responses in rodents may not be relevant to primates. In addition, the established cell culture method represents a useful tool to study the physiological and/or pathological roles of GLP1 and GLP1R agonists on normal, non-transformed primary C-cells from rats and man.
This Publication used the Rat Calcitonin EIA kit (RK-014-06) from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for measurement of calcitonin concentration.
Boess F, Bertinetti-lapatki C, Zoffmann S, et al. Effect of GLP1R agonists taspoglutide and liraglutide on primary thyroid C-cells from rodent and man. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013;50(3):325-36.
AIM: The purpose of this study was to develop a new orally delivered nanoparticulate system to improve the bioavailability of salmoncalcitonin (sCT).MATERIALS & METHODS: Four sCT-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) were prepared successfully by micelle-double emulsiontechnique via either the sole use of stearic acid (SA) or the combined use of SA and triglycerides (including tripalmitin [TP], trimyristin or trilaurin).RESULTS: Compared with other SLNs, the combination of SA and TP could not only significantly improve the colloidal stability of SLNs and enhance the drug stability in the simulated intestinal fluids, but also intensively increase the intracellular uptake of drugs compared with the other SLNs (p < 0.05). The mechanism of internalization was an active transport involved in clathrin- and caveolae-dependent endocytosis. In vivo, the sCT SLNs prepared with SA and TP exhibited the highest reduction of plasma Ca(2+) level (17.44 ± 3.68%) with a bioavailability of 13.01 ± 3.24%.CONCLUSION: The SLNs formed by SA and TP as the solid lipids may be a promising carrier for oral delivery of peptide drugs.
This Publication used the salmon Calcitonin RIA kit (RK-014-09) from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for measurement of calcitonin concentration.
Chen C, Fan T, Jin Y, et al. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013;8(7):1085-100.
Calcitonin is used as a second line treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, but widespread acceptance is somewhat limited by subcutaneous and intranasal routes of delivery. This study attempted to enable intestinal sCT absorption in rats using the mild surfactant, tetradecyl maltoside (TDM) as an intestinal permeation enhancer. Human Caco-2 and HT29-MTX-E12 mucus-covered intestinal epithelial monolayers were used for permeation studies. Rat in situ intestinal instillation studies were conducted to evaluate the absorption of sCT with and without 0.1 w/v% TDM in jejunum, ileum and colon. TDM significantly enhanced sCT permeation across intestinal epithelial monolayers, most likely due to combined paracellular and transcellular actions. In situ, TDM caused an increased absolute bioavailability of sCT in rat colon from 1.0% to 4.6%, whereas no enhancement increase was observed in ileal and jejunal instillations. Histological analysis suggested mild perturbation of colonic epithelia in segments instilled with sCT and TDM. These data suggest that the membrane composition of the colon is different to the small intestine and that it is more amenable to permeation enhancement. Thus, formulations designed to release payload in the colon could be advantageous for systemic delivery of poorly permeable molecules.
This Publication used the salmon Calcitonin EIA kit (EK-014-09) from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for measurement of calcitonin concentration.
Petersen SB, Nielsen LG, Rahbek UL, Guldbrandt M, Brayden DJ. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;48(4-5):726-34.
The most common cause of hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a nonfunctional vasopressin (VP) receptor type 2 (V2R). Calcitonin, another ligand of G-protein–coupled receptors, has a VP-like effect on electrolytes and water reabsorption, suggesting that it may affect AQP2 trafficking. Here, calcitonin increased intracellular cAMP and stimulated the membrane accumulation of AQP2 in LLC-PK1 cells. Pharmacologic inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA) and deficiency of a critical PKA phosphorylation site on AQP2 both prevented calcitonin-induced membrane accumulation of AQP2. Fluorescence assays showed that calcitonin led to a 70% increase in exocytosis and a 20% decrease in endocytosis of AQP2. Immunostaining of rat kidney slices demonstrated that calcitonin induced a significant redistribution of AQP2 to the apical membrane of principal cells in cortical collecting ducts and connecting segments but not in the inner stripe or inner medulla. Calcitonin-treated VP-deficient Brattleboro rats had a reduced urine flow and two-fold higher urine osmolality during the first 12 hours of treatment compared with control groups. Although this VP-like effect of calcitonin diminished over the following 72 hours, the tachyphylaxis was reversible. Taken together, these data show that calcitonin induces cAMP-dependent AQP2 trafficking in cortical collecting and connecting tubules in parallel with an increase in urine concentration. This suggests that calcitonin has a potential therapeutic use in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Appleyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-60.
No References
| Catalog# | Product | Size | Price | Buy Now |
|---|
Social Network Confirmation