
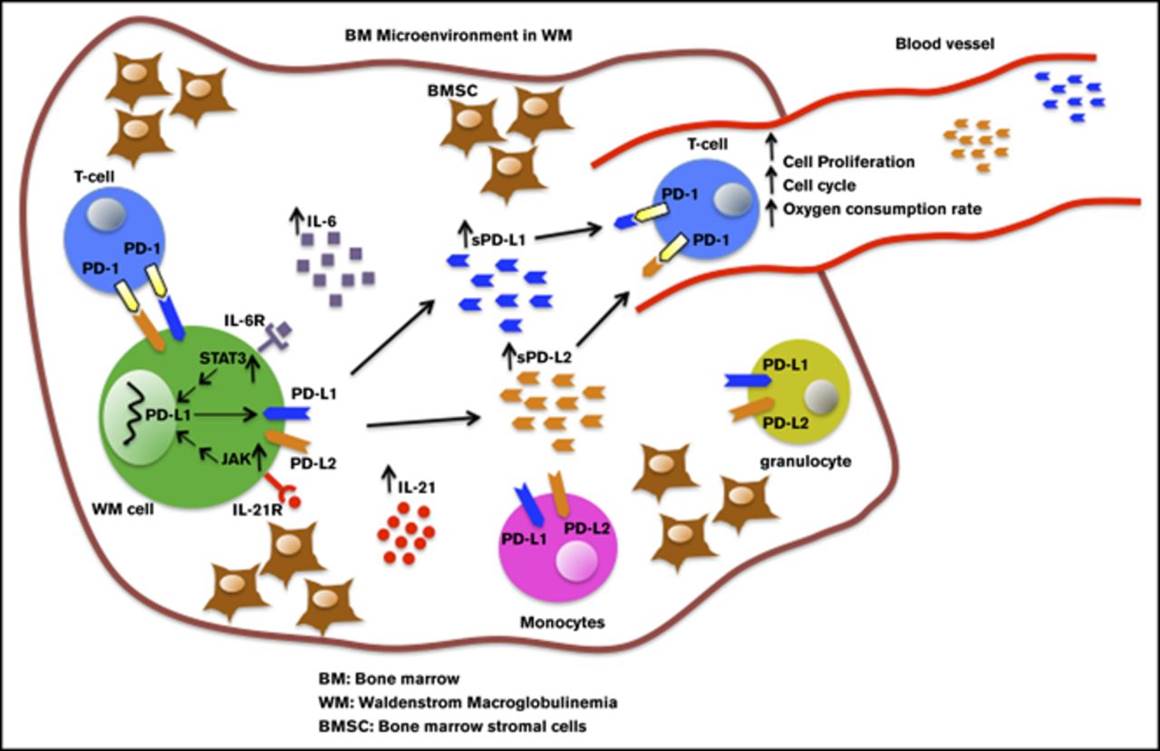
Although immune checkpoint molecules regulate the progression of certain cancers, their significance in malignant development of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM), an incurable low-grade B-cell lymphoma, remains unknown. Recently, cytokines in the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment are shown to contribute to the pathobiology of WM. Here, we investigated the impact of cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-21, on immune regulation and particularly on the programmed death-1 (PD-1) and its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. We showed that IL-21, interferon γ, and IL-6 significantly induced PD-L1 and PD-L2 gene expression in WM cell lines. Increased PD-L1 and PD-L2 messenger RNA was also detected in patients' BM cells. Patients' nonmalignant BM cells, including T cells and monocytes, showed increased PD-L1, but minimal or undetectable PD-L2 surface expression. There was also very modest PD-L1 and PD-L2 surface expression by malignant WM cells, suggesting that ligands are cleaved from the cell surface. Levels of soluble ligands were higher in patients' BM plasma and blood serum than controls. Furthermore, IL-21 and IL-6 increased secreted PD-L1 in the culture media of WM cell lines, implying that elevated levels of soluble PD-1 ligands are cytokine mediated. Soluble PD-1 ligands reduced T-cell proliferation, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase and cyclin A levels, mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate production, and spare respiratory capacity. In conclusion, we identify that soluble PD-1 ligands are elevated in WM patients and, in addition to surface-bound ligands in WM BM, could regulate T-cell function. Given the capability of secreted forms to be bioactive at distant sites, soluble PD-1 ligands have the potential to promote disease progression in WM.
Jalali S, Price-Troska T, Paludo J et al., Blood Adv. 2018 Aug 14;2(15):1985-1997. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018021113.
BACKGROUND: PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 belong to the co-inhibition molecules, which can downregulate immune responses. The PD-L1polymorphism and the level of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) were investigated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).METHODS: A total of 288 NSCLC patients and 300 controls were enrolled. An A/C polymorphism at position 8923 in the PD-L1 gene was genotyped using the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method.RESULTS: The prevalence of the 8923C allele was significantly higher in NSCLC patients than controls (10.2% versus 5.3%, p = 0.002, odds ratio 2.03, 95% confidence interval 1.30-3.17; data were adjusted for age and sex). NSCLC patients also showed increased plasma levels of sPD-L1 compared to controls (1.92 ng/mL versus 0.91 ng/mL, p<0.001). Furthermore, lung adenocarcinoma patients had higher sPD-L1 levels than patients with squamous cell carcinoma (p<0.01). However, no association was observed between the different genetic variants and plasma concentrations of sPD-L1.CONCLUSIONS: The PD-L1 8923A/C polymorphism could be associated with increased susceptibility to NSCLC. Plasma levels of sPD-L1 are significantly increased in NSCLC patients, especially those with adenocarcinoma.
Cheng S, Zheng J, Zhu J et al., Int J Biol Markers. 2015 Nov 11;30(4):e364-8. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000170.
Understanding mechanisms of late/acquired cancer immunotherapy resistance is critical to improve outcomes; cellular immunotherapy trials offer a means to probe complex tumor-immune interfaces through defined T cell/antigen interactions. We treated two patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma with autologous Merkel cell polyomavirus specific CD8+ T cells and immune-checkpoint inhibitors. In both cases, dramatic remissions were associated with dense infiltration of activated CD8+s into the regressing tumors. However, late relapses developed at 22 and 18 months, respectively. Here we report single cell RNA sequencing identified dynamic transcriptional suppression of the specific HLA genes presenting the targeted viral epitope in the resistant tumor as a consequence of intense CD8-mediated immunologic pressure; this is distinguished from genetic HLA-loss by its reversibility with drugs. Transcriptional suppression of Class I loci may underlie resistance to other immunotherapies, including checkpoint inhibitors, and have implications for the design of improved immunotherapy treatments.
Paulson KG, Voillet V, Mcafee MS, et al. Acquired cancer resistance to combination immunotherapy from transcriptional loss of class I HLA. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3868.
BACKGROUND: Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive neoplasm, which is often associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV). Programmed death-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 are key players of the tumor microenvironment (TME).METHODS: Fourteen paraffin-embedded tissue samples of MCC were stratified by their MCPyV detection. Apart from PD-L1 and PD-1, the TME was further characterized for the expression of CD33, FOXP3 and MxA.RESULTS: We observed PD-1 in 2 of 12 tumors. PD-L1 expression by tumor cells was found in 7 of 8 MCPyV(+) samples and was detected particularly in the periphery. The tumor cells were surrounded by a shield of PD-L1/CD33 immune cells. Expression of PD-L1 by the tumor cells was higher in areas with a denser immune infiltrate. CD33(+) cells without direct tumor contact were PD-L1 negative. Only a low number of FOXP3(+) regulatory T-cells was admixed. Tumor cells of MCPyV(-) samples were mostly PD-L1 negative.CONCLUSIONS: Our data demonstrate that PD-L1 expression occurs in tumor and immune cells, in areas in which they are close in contact. Interferon seems to play a role in this interaction. We postulate that PD-L1(+)/CD33(+) cells shield the tumor against attacking PD-1(+) immune cells. Therefore, next to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, blockade of CD33 seems to be a promising therapeutic approach.
Mitteldorf C, Berisha A, Tronnier M, Pfaltz MC, Kempf W. PD-1 and PD-L1 in neoplastic cells and the tumor microenvironment of Merkel cell carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44(9):740-746.
Virus infection contributes to nearly 15% of human cancers worldwide. Many of the oncogenic viruses tend to cause cancer in immunosuppressed individuals, but maintain asymptomatic, persistent infection for decades in the general population. In this review, we discuss the tactics employed by two small DNA tumor viruses, Human papillomavirus (HPV) and Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV), to establish persistent infection. We will also highlight recent key findings as well as outstanding questions regarding the mechanisms by which HPV and MCPyV evade host immune control to promote their survival. Since persistent infection enables virus-induced tumorigenesis, identifying the mechanisms by which small DNA tumor viruses achieve latent infection may inform new approaches for preventing and treating their respective human cancers.
Krump NA, Liu W, You J. Mechanisms of persistence by small DNA tumor viruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2018;32:71-79.
| Catalog# | Product | Standard Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 027-60 | C-terminal-PD-1 (55-94) (Human) | 100 µg | $490 |
| 027-62 | C-terminal-PD-1 (78-113) (Human) | 100 µg | $428 |
Social Network Confirmation