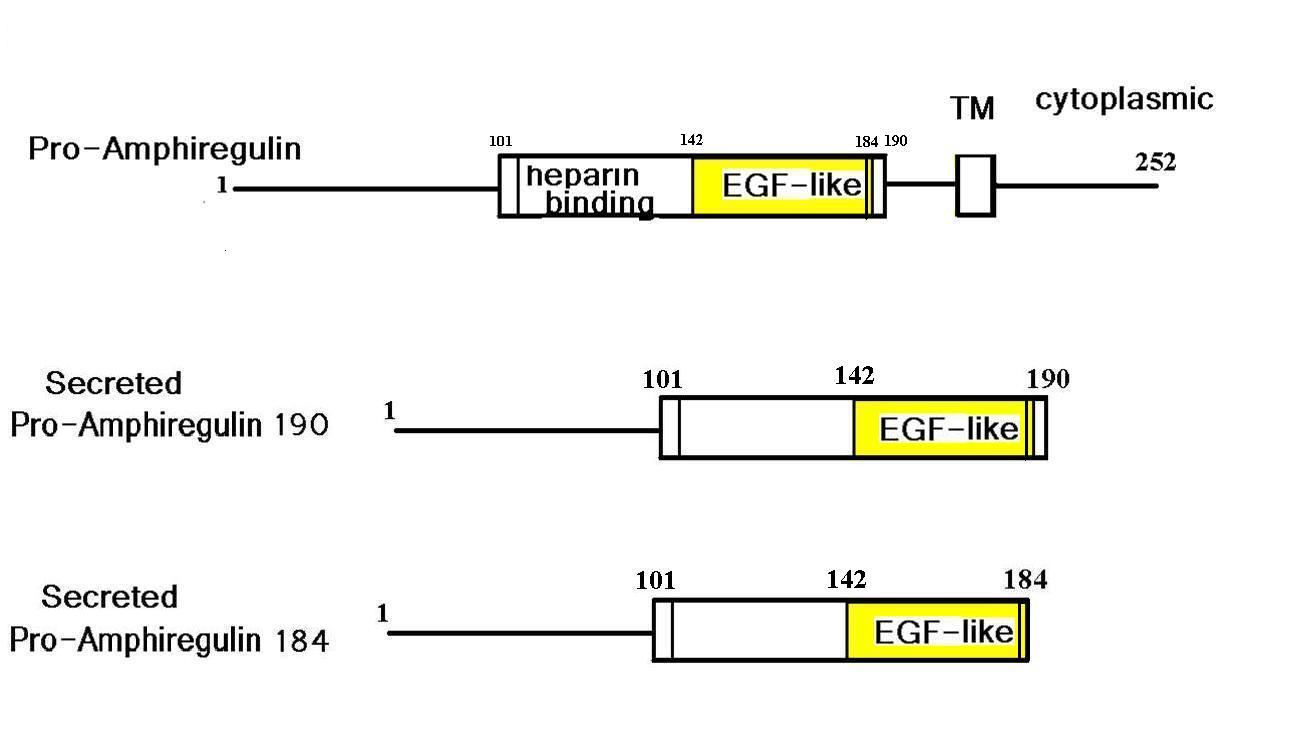
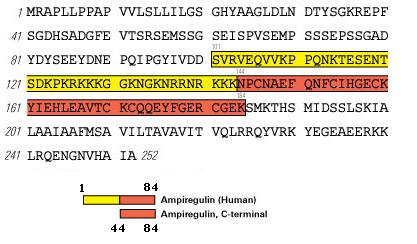
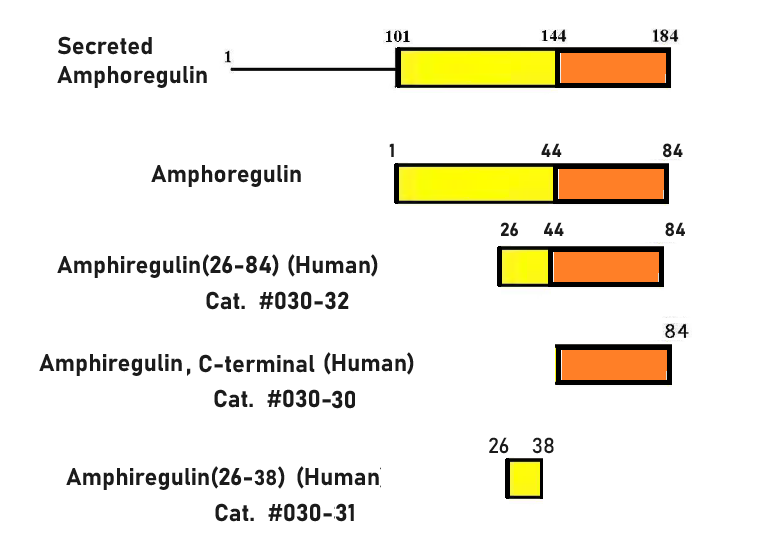
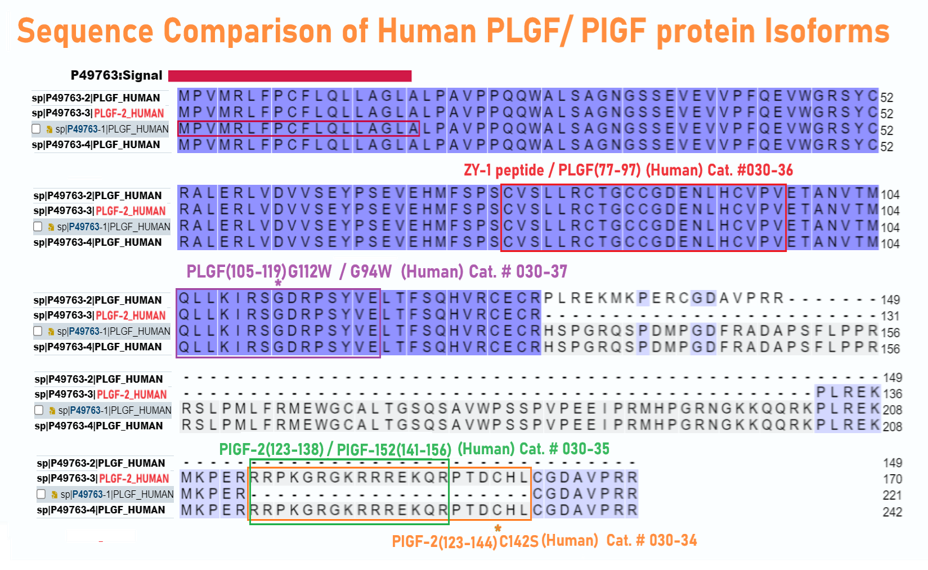
Abstract: Among therapeutic proteins, cytokines and growth factors have great potential for regenerative medicine applications. However, these molecules have encountered limited clinical success due to low effectiveness and major safety concerns, highlighting the need to develop better approaches that increase efficacy and safety. Promising approaches leverage how the extracellular matrix (ECM) controls the activity of these molecules during tissue healing. Using a protein motif screening strategy, we discovered that amphiregulin possesses an exceptionally strong binding motif for ECM components. We used this motif to confer the pro-regenerative therapeutics platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) a very high affinity to the ECM. In mouse models, the approach considerably extended tissue retention of the engineered therapeutics and reduced leakage in the circulation. Prolonged retention and minimal systemic diffusion of engineered PDGF-BB abolished the tumour growth-promoting adverse effect that was observed with wild-type PDGF-BB. Moreover, engineered PDGF-BB was substantially more effective at promoting diabetic wound healing and regeneration after volumetric muscle loss, compared to wild-type PDGF-BB. Finally, while local or systemic delivery of wild-type IL-1Ra showed minor effects, intramyocardial delivery of engineered IL-1Ra enhanced cardiac repair after myocardial infarction by limiting cardiomyocyte death and fibrosis. This engineering strategy highlights the key importance of exploiting interactions between ECM and therapeutic proteins for developing effective and safer regenerative therapies.
Alshoubaki YK, Lu YZ, Legrand JMD, et al. A superior extracellular matrix binding motif to enhance the regenerative activity and safety of therapeutic proteins. npj Regen Med. 2023;8(1):25.
Abstract: Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) is one of the most important factors for bone tissue formation. However, its use over the past decade has been associated with numerous side effects. This is due to the fact that recombinant human (rh) BMP-2 has several biological functions, as well as that non-physiological high dosages were commonly administered. In this study, we synthesized a novel BMP-2-related peptide (designated P28) and fused a mutant domain in placenta growth factor-2...
Xiong Z, Cui W, Sun T, et al. Sustained delivery of PlGF-2. RSC Adv. 2020;10(12):7289-7300.
Abstract: Corneal neovascularization (NV) is one of the major sight-threatening pathological changes caused by corneal diseases. Current therapeutics generate various adverse effects. Small peptides derived from endogenous protein display certain advantages. This study aims to evaluate the anti-angiogenic effect and molecular mechanism of a novel peptide ZY-1, derived from placental growth factor-1 (PlGF-1), on corneal NV by topical administration, and to investigate its safety profile after long-term treatment. CCK-8 assay and tube formation assay were used to evaluate the effect of ZY-1 on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
Lu Y, Zheng Y, Ai J, Xu X. Therapeutic effects of a novel pigf-1 derived peptide, zy-1, on corneal neovascularization in vitro and in vivo. Discovery Medicine. 2016;21(117):349-361.
| Catalog# | Product | Standard Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 030-31 | AREG(26-38) / Amphiregulin(26-38) (Human) | 200 μg | $152 |
| 030-32 | AREG(26-84) / Amphiregulin(26-84) (Human) | 100 μg | $520 |
| 030-30 | Amphiregulin, C-terminal (Human) | 100 µg | $444 |
| 030-34 | PIGF-2(123-144) C142S (Human) | 200 μg | $208 |
| 030-37 | PLGF(105-119) G112W / G94W (Human) | 200 μg | $163 |
| 030-35 | PlGF-2(123-138) / PlGF152(141-156) (Human) | 100 μg | $173 |
| 030-36 | ZY-1 peptide / PLGF(77-97) (Human) | 100 μg | $173 |
Social Network Confirmation